Cleveland Clinic Study Shows Flu Vaccine has Negative Efficacy
BY JEFF SKINNER
STATEWIDE - As we move deeper into cold season, many Americans are considering how best to protect themselves from illness. However, a recent study published puts significant doubt on the medical establishments leading tool deployed to patients.
According to a study conducted by Cleveland Clinic, which examined recipients of the influenza vaccine from 2024-2025 flu season, recipients of the vaccine were 26 percent more likely to get sick compared to those who did not receive it. The study comes during a time when Americans by and large are becoming increasingly skeptical of vaccine science in general.
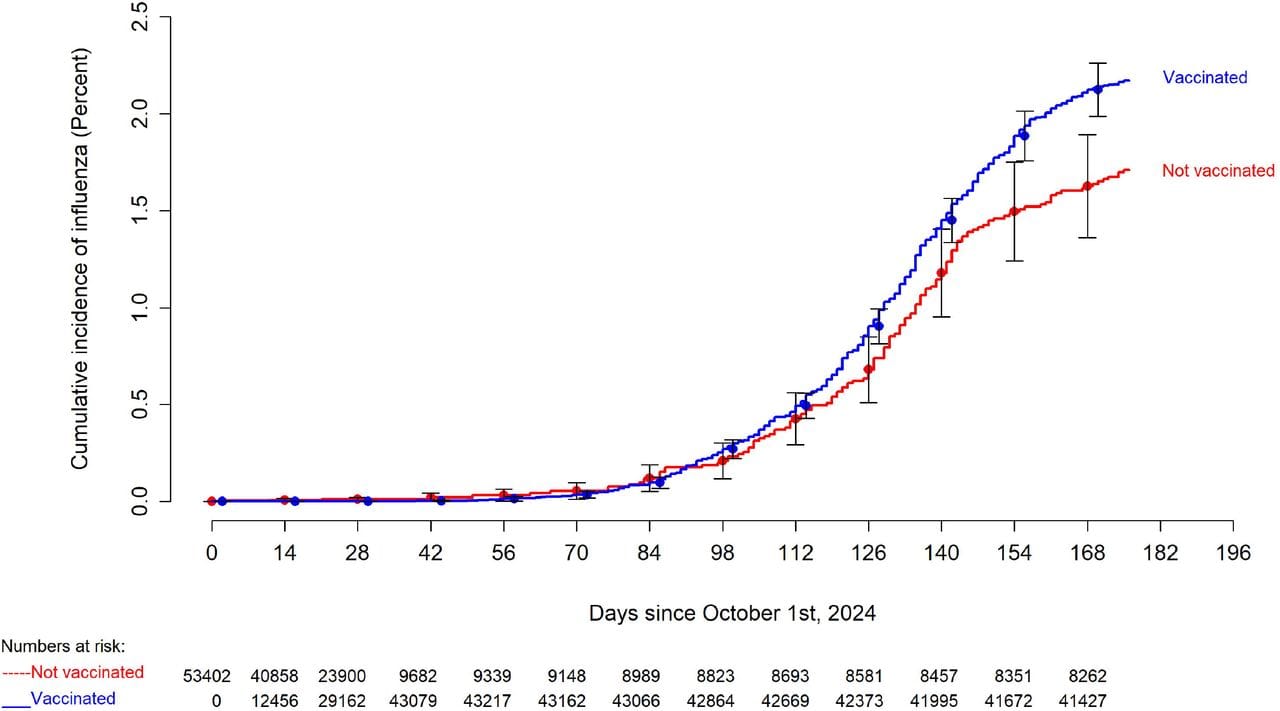
The study, which was published in April, looked at 53,402 employees at the Cleveland Clinic hospital network, with 43,857 (82.1%) having received the influenza vaccine by the end of the study. Based on the reported data, The cumulative incidence of influenza was similar for the vaccinated and unvaccinated cohorts in the early portions of the study however over the course of the study the cumulative incidence of influenza increased more rapidly among the vaccinated than the unvaccinated. When researchers adjusted for age, sex, clinical nursing job, and employment location, the risk of influenza was significantly higher for the vaccinated compared to the unvaccinated cohorts showing a significant negative efficacy of the vaccine.
Based on the reported data, those who received the vaccine were 26.9%more likely to contract illness than those who did not receive the injection.
The research from Cleveland Clinic calls into question longstanding 'wisdom' surrounding vaccine science in the industry, which has historically relied on guesswork to determine what strain of influenza would be circulating as well as the concept of including adjuvants used to spur immune responses. Adjuvants are compounds in the vaccine used to induce inflammatory and immune responses to get the immune system to recognize the injected attenuated virus as a systemic threat. However, many in the scientific community have linked the adjuvant based inflammatory responses to long-term autoimmune issues.
The Influenza vaccine regularly contains adjuvants, such as Aluminum, which has long been studied as a contributing compound to neurodegenerative ailments such as Alzheimer's and dementia in adults. The root of this comes from the inflammatory response caused when aluminum comes in contact with brain cells leading to issues with spatial learning and long‐term potentiation when the adjuvant nanoparticles cross the blood-brain barrier. In short, based on available research across the aforementioned Cleveland Clinic study and others related to the compounds contained in the vaccine, those who received the flu vaccine are more likely to get sick with flu and have long-term neurodegenerative disorders, shortening their lifespan.
Despite this evidence, the CDC still lists on their website that Americans by and large take the flu shot. Many naturopathic practitioners suggest patients read through available research and come to their own, informed conclusions knowing the risks.




